The coastal population of Mauritius is a significant demographic feature. It plays a pivotal role in the island nation's economic, social and cultural, environmental dynamics and resilience. Fostering coastal populations and addressing the challenges they face is essential for sustainable development.
A substantial proportion of Mauritius' population resides in coastal regions, leading to population concentration and urbanization along the coast. This demographic phenomenon is particularly evident in urban areas like Port Louis, which serves as the nation's economic and administrative hub, and also in tourist-centric regions such as Grand Baie and Flic en Flac. The coastal population significantly drives the country's economy. Coastal regions are home to major economic activities, including tourism, fishing, trade, and port operations. The tourism sector, in particular, benefits from the allure of coastal attractions, including beaches at Trou aux Biches and the vibrant coral reefs near Blue Bay. Balancing economic development with environmental conservation and the well-being of coastal populations presents a complex challenge. Sustainable development and coastal zone management are essential to address these challenges. Coastal Population and EconomyCoastal areas, being hubs of economic activity and tourism, are melting pots of cultural diversity. The coastal population includes people from various ethnic backgrounds, contributing to the rich cultural tapestry of the island. Cultural events such as the Sega festival in Le Morne and the diverse cuisine in Mahebourg reflect this diversity. The coastal population benefits from the economic opportunities presented by tourism, which creates jobs and income. Coastal areas are not only places of residence but also sites for recreational activities, contributing to a higher quality of life for residents. Coastal areas receive significant investments in infrastructure and services, such as healthcare, education, and transportation, due to their higher population density. For example, the development of the Metro Express linking coastal areas enhances connectivity and access to services. Ensuring equitable distribution of these resources remains a priority for the government. Coastal Population and EnvironmentThe coastal population is inherently linked to the vulnerability and resilience of Mauritius in the face of natural hazards, such as tropical cyclones, rising Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs) and rising sea levels. Many coastal communities, such as those in Albion and Bel Ombre, are at risk of flooding and erosion, emphasizing the importance of disaster preparedness and climate resilience. Coastal communities have historically displayed resilience in the face of natural disasters. Their ability to adapt and recover from adverse events is a testament to their resourcefulness and determination. The proximity of coastal populations to fragile ecosystems like coral reefs and mangroves can lead to environmental impacts. Issues such as overfishing in the lagoons of Trou d'Eau Douce, coral degradation along the northern reefs, and habitat destruction are challenges that are being addressed through sustainable management and conservation efforts. Coastal hazards such as oil spill affect the fishermen community and marine biodiversity. |
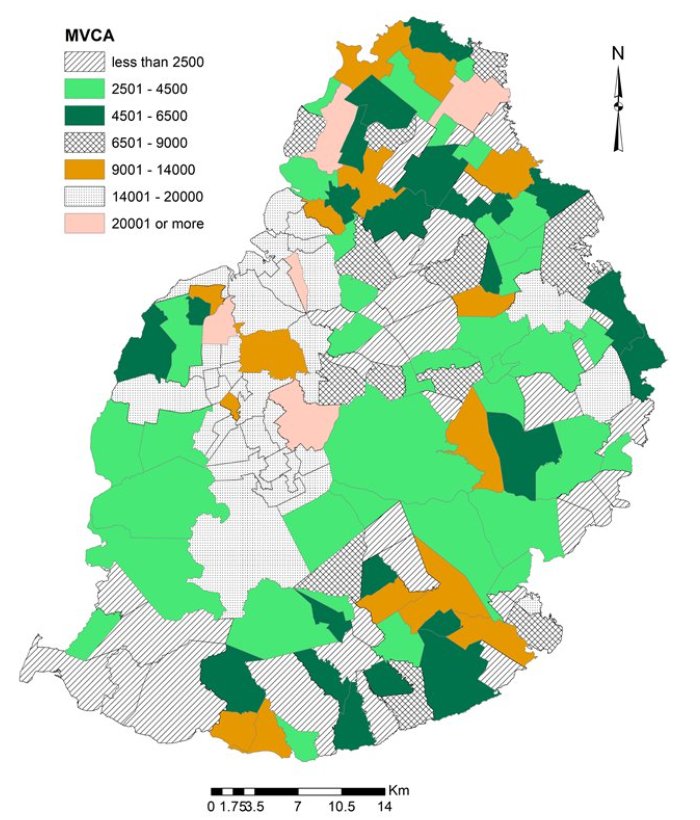
Mid - year population by Municipal Ward/Village Council Area (MVCA) - Island of Mauritius 2022 (source: SM) |