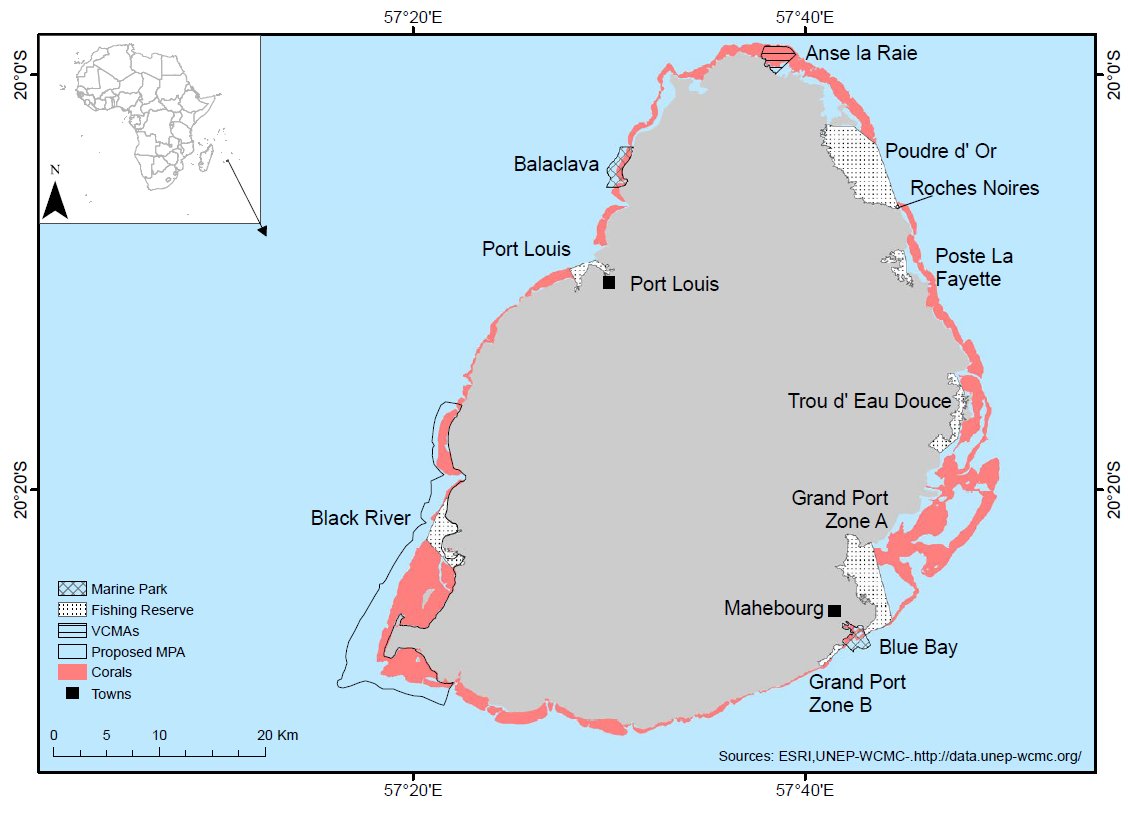
MAURITIUS MPAs (7190 ha) | ||
Of the 8 MPAs established in Mauritius, two (2) are designated as Marine Parks and six (6) as Fishing Reserves (see Figure). These MPAs encompass both coastal and pelagic environments, including the lagoon and coral reefs, and extend slightly beyond the reef boundaries.
There are discussions on reevaluating the effectiveness of MPAs in Mauritius, focusing on designing strict conservation zones that minimize impact on local communities. Additionally, any developments that might affect these protected areas are scrutinized under the Outline Planning Scheme to ensure they do not adversely affect sensitive marine environments.
| 
| |
MAURITIUS NON-FORMAL MPAs– VOLUNTARY MARINE CONSERVATION AREAS | ||
The introduction of Voluntary Marine Conservation Areas (VMCAs) is a relatively new development in Mauritius, spearheaded by Reef Conservation, an NGO active in the northern part of the island focused on protecting coastal and marine environments. VMCAs are specific areas within the lagoon where local resource users and coastal communities voluntarily agree to refrain from extractive or destructive activities. The primary goals of these areas are to safeguard marine biodiversity and aid in the regeneration of marine life both within the VMCAs and the adjacent lagoon areas. Although these conservation sites are driven by community initiatives, they currently lack formal legal recognition and, therefore, do not possess any legal status.
| Following feasibility studies, 2 VMCAs were established in the north of Mauritius:
Initial funding was from the Indian Ocean Commission: Regional Coastal Management Programme (RECOMAP) in 2008 with further funding in 2012 and 2016 from the GEF Small Grants Programme of the UNDP and local private sector partners. These VMCAs were created using a participatory approach, involving local stakeholders such as boat operators, fishers, village representatives, and volunteers who collectively form a VMCA committee responsible for management at each site. Management practices include regular and thorough monitoring of the marine ecosystem, conducting awareness-raising activities, and ensuring compliance with the established rules. Additional initiatives involve training local community members as eco-guides and in aspects of marine resource management and marine ecology and conservation. | |


