Overview of Food-Borne Diseases in Mauritius | ||
Public Health ChallengesFood-borne diseases represent a significant public health issue in Mauritius, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. These diseases result from the ingestion of food or beverages contaminated with harmful pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Contamination can occur at multiple stages, including production, processing, distribution, and preparation, making it a complex challenge to manage. Economic and Tourism ImpactThe impact of food-borne diseases is not limited to health alone but extends to economic consequences, particularly affecting the tourism sector—a crucial component of Mauritius's economy. Tourists may be particularly vulnerable to food-borne diseases due to exposure to new cuisines and different food handling practices. The prevalence of these diseases can deter tourists, impacting the reputation of Mauritius as a safe travel destination. Environmental Contributions to RiskEnvironmental factors in Mauritius, such as its tropical climate, can also contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. High temperatures and humidity are ideal conditions for the growth and proliferation of many pathogens, thereby increasing the risk of food spoilage and contamination. Seasonal variations influence the rate of food-borne infections, with a higher incidence typically observed during the warmer months when bacteria grow more rapidly. Globalization and Food SafetyThe food supply chain in Mauritius is diverse, involving local production and international imports, which introduces multiple points where contamination can occur. The globalization of food trade means that food-borne pathogens can easily cross national boundaries, necessitating stringent controls on food imports and exports. Regulatory and Preventive MeasuresMauritian authorities are tasked with continuously updating and enforcing food safety regulations to keep pace with these challenges. This involves not only managing local food production practices but also overseeing the safety of imported foods. Public awareness and education about safe food handling practices are crucial for preventing food-borne diseases and ensuring that both residents and visitors can enjoy the local cuisine without health risks. |  Environmental factors in Mauritius, such as its tropical climate, can also contribute to the prevalence of these diseases. High temperatures and humidity are ideal conditions for the growth and proliferation of many pathogens, thereby increasing the risk of food spoilage and contamination. | |
Status of Environmental Health in terms of Food-borne Diseases | ||
Continual efforts are made in Mauritius to improve food safety and prevent foodborne illnesses. The implementation of comprehensive regulations, regular inspections, food safety training, surveillance systems, and consumer education contribute to maintaining a high level of environmental health in relation to foodborne illnesses in the country. | The status of environmental health in Mauritius with regard to foodborne illnesses and their prevention can be described as follows: 1. Regulatory Framework: Mauritius has established a robust regulatory framework to ensure food safety. The Food Act of 2022, the Food Regulations of 2022 and the Food Standards Agency Act 2022 set standards and guidelines for food processing, transportation, storage, and handling. The Ministry of Health and Wellness, in collaboration with the Food Safety Authority, oversees the implementation and enforcement of these regulations. 2. Inspections and Monitoring: Regular inspections of food establishments, including restaurants, hotels, and food processing facilities, are carried out to assess their compliance with food safety standards. These inspections help identify potential risks and ensure that proper food handling practices are followed. Monitoring is also conducted to detect any outbreaks of foodborne illnesses and initiate timely intervention. 3. Food Safety Training: Efforts are made to enhance the knowledge and skills of food handlers in Mauritius. Training programs and workshops are conducted to educate food industry workers about proper hygiene, safe food handling practices, and the prevention of cross-contamination. This helps minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses caused by mishandling of food. 4. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP): Implementation of the HACCP system is encouraged in various food establishments in Mauritius. This internationally recognized system identifies potential hazards in the food production process and establishes critical control points to ensure the prevention, reduction, or elimination of those hazards. HACCP helps ensure that foodborne illness risks are systematically managed and controlled. 5. Surveillance and Outbreak Response: Surveillance systems are in place to monitor and identify foodborne illness outbreaks in Mauritius. When outbreaks occur, prompt investigation, including laboratory testing, is conducted to identify the source of contamination and take appropriate measures to prevent further spread. This involves collaboration between the Ministry of Health and Wellness, the Food Safety Authority, and other relevant agencies. 6. Consumer Education: Mauritius promotes consumer education and awareness about safe food practices. Information campaigns, public service announcements, and educational materials are used to educate the public on proper food handling, storage, and preparation. This empowers consumers to make informed choices and take necessary precautions to prevent foodborne illnesses. 7. Food Import Controls: Mauritius implements strict controls on imported food items to ensure their safety. Inspections are carried out at ports of entry to verify compliance with import regulations and standards. This helps prevent the introduction of contaminated or unsafe food products into the country. 8. Collaboration and International Standards: Mauritius actively participates in regional and international networks related to food safety. It collaborates with organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and the World Trade Organization (WTO) to strengthen its food safety systems and align them with international standards. | |
The Role of Environmental Factors in Food Safety | ||
In Mauritius, environmental factors play a significant role in the prevalence and spread of food-borne diseases. The island's tropical climate, seasonal variations, and geographical characteristics influence the conditions that promote the growth of pathogens in food. Understanding these environmental factors is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and safeguarding public health.  | The interaction between environmental factors and food-borne diseases in Mauritius is complex and multifaceted. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach - see below. t Key Environmental Factors Influencing Food-Borne Diseases 1. Climate Conditions
2. Water Supply and Quality
3. Agricultural Practices
4. Waste Management
5. Environmental Changes and Natural Disasters
| |
Common Food-Borne Pathogens | ||
Managing these pathogens requires a comprehensive approach that includes public health education, regulatory enforcement on food safety standards, and cooperation between food suppliers and consumers. Awareness and education about these common food-borne pathogens are vital to reducing the incidence of food-borne diseases in Mauritius, safeguarding both public health and the tourism industry. 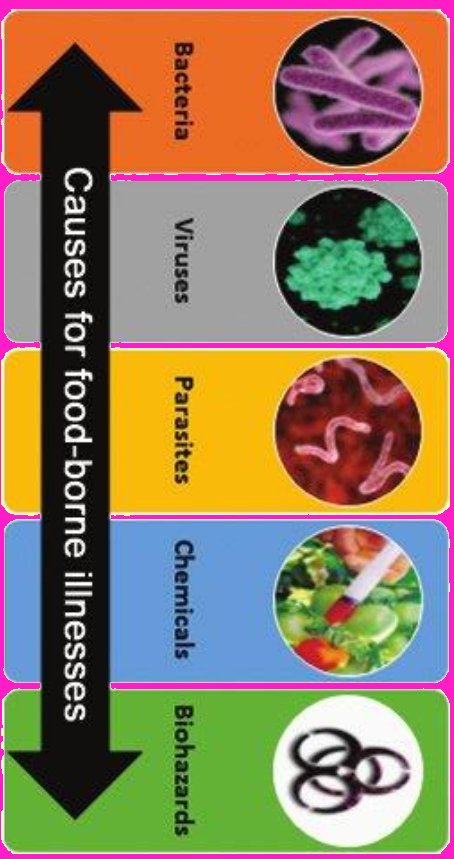 | 1. Salmonella
2. Campylobacter
3. Escherichia coli (E. coli)
4. Listeria
| |
Challenges in Managing Food-Borne Diseases in Mauritius | ||
| Addressing the challenges of managing food-borne diseases in Mauritius requires a multi-dimensional approach that includes strengthening infrastructure, enhancing public education, improving regulatory frameworks, and embracing technological advancements. Collaborative efforts across government, industry, and community levels are essential to effectively mitigate these risks and protect public health. | 1. Infrastructure Limitations
2. Climate and Environmental Factors
3. Economic and Resource Constraints
4. Public Awareness and Behavior
5. Regulatory and Enforcement Challenges
6. Globalization of Food Supply
7. Technological and Innovation Gaps
| |
Preventive Measures | ||
The prevention of food-borne diseases in Mauritius relies on a robust and proactive approach that encompasses regulatory oversight, public education, infrastructure improvements, and the adoption of new technologies. By strengthening these areas, Mauritius can better protect its citizens and visitors from the risks associated with food-borne pathogens, thereby supporting public health and maintaining the integrity of its tourism industry. | Preventing food-borne diseases requires a multi-faceted approach that involves the combined efforts of government agencies, food industry stakeholders, and the general public. Here are some expanded preventive measures to mitigate the risk of food-borne illnesses in Mauritius: 1. Regulatory Enforcement and Compliance
2. Public Health Education and Awareness
3. Infrastructure Improvements
4. Technological Innovations
5. Personal Hygiene and Safe Food Practices
6. Collaboration and Partnership
| |
CHECKLIST for safe food shopping, storage, and preparation | ||
Shopping
Storage
Preparation
| ||


