Discover the ecological importance of Rodrigues's coastline and marine environments, the challenges they face, and the strategies needed to mitigate these issues effectively. It also outlines Rodrigues's comprehensive approach to managing its coastal and marine resources, emphasizing the integration of environmental sustainability into economic activities to ensure the long-term viability of its ocean economy.
Overview of Coastal and Marine Resources of Rodrigues | |
Coastline FeaturesRodrigues' coastline extends approximately 67 kilometers, featuring diverse topographical elements such as 70% rocky coasts, 21% silt-clay coasts, and 9% coral sand beaches. Notable are the sandy islets, Ile aux Sables and Ile aux Cocos, which enhance the region's natural beauty and biodiversity. Coral Reefs and BiodiversityThe island hosts the most extensive and well-preserved coral reefs within the Mascarene Islands, boasting a high living coral cover. These reefs support a vast array of marine life, including 493 fish species, 175 gastropod species, and 138 coral species. Despite this rich biodiversity, Rodrigues exhibits lower species diversity compared to neighboring regions. Annual monitoring of these reefs has revealed a concerning decline in coral cover, primarily due to rising sea temperatures and human activities. In response, initiatives like the coral planting program have been launched to rehabilitate and strengthen the resilience of these vital ecosystems. Environmental Sensitivity and ChallengesProtected AreasSignificant portions of Rodrigues' lagoon ecosystem, which includes coral reefs, seagrass beds, and algal beds, are classified as environmentally sensitive and are crucial for maintaining ecological balance. MangrovesThe thriving mangroves of Rodrigues play a crucial role in enhancing the island's ecological stability, facing minimal anthropogenic threats. Threats to Marine ResourcesThe marine resources of Rodrigues are in continuous decline, influenced by pollution, sedimentation, harmful fishing practices, and poorly planned coastal construction. Natural phenomena like cyclones and climate change further exacerbate overfishing and habitat degradation. Marine Resource Management and ConservationLegislative and Management ChallengesManagement efforts to safeguard Rodrigues' marine environment are often fragmented and lack sufficient capacity, posing significant challenges to effective conservation. Fishing Practices and ImpactsLocal fishing methods frequently harm coral structures and algal matting, leading to reduced fish sizes and overall catches despite intensified fishing efforts. The octopus fishery, in particular, has experienced significant stock fluctuations, with sharp declines in the early 2010s. A management strategy that included implementing a closed fishing season from August 15 to October 15, aligning with the octopus spawning season, has successfully enhanced both the size and quantity of catches, showcasing effective resource management. Research, Monitoring, and Enforcement GapsMonitoring and ControlEffective Monitoring, Control, and Surveillance (MCS) are hampered by weak enforcement of legal measures and insufficient human resources, allowing illegal fishing practices to persist. Research and Data ShortagesThere is an acute shortage of technical personnel and facilities for research, particularly in collecting baseline data on mangrove biodiversity, which is essential for informed management decisions. Policy Needs and Future DirectionsPolicy GapsRodrigues requires comprehensive policies to address issues like lagoon sedimentation from construction activities and to enhance the management of marine reserves. Sustainable PracticesPromoting sustainable fishing practices, such as outer lagoon fishing and the use of Fish Aggregating Devices (FADs), along with improving management of marine protected areas, is essential for reducing environmental impacts and promoting long-term sustainability. Conclusions and Future DirectionsThe coastal and marine resources of Rodrigues are invaluable to the island’s economy and ecological health. Ensuring the sustainability of these resources hinges on continuous monitoring, adaptive management, and strong community engagement. Future efforts should focus on enhancing ecosystem resilience through comprehensive policy measures and increased stakeholder participation, ensuring the preservation of Rodrigues' unique marine and coastal environments. This balanced approach must accommodate both conservation and development needs to maintain the island's ecological integrity. | 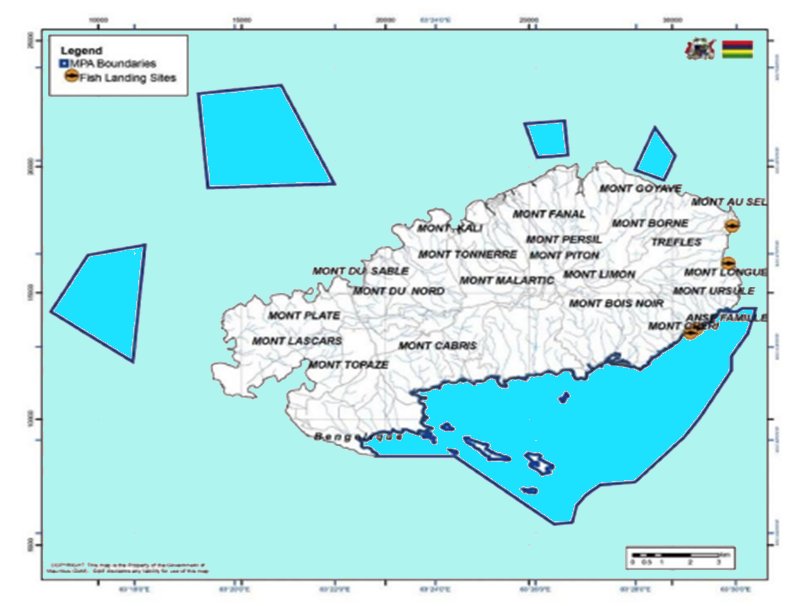 Marine protected areas in Rodrigues |
Coastal and Marine Resources Management |
Overview of Ocean Economy and Sustainability Efforts
- Rodrigues Island exemplifies the concept of the Ocean Economy (OE) by integrating various marine and coastal sectors such as fisheries, tourism, and transportation into a cohesive sustainable development framework. The island has developed a "sensitive" tourism model and taken steps to manage lagoon restoration and octopus fisheries effectively. These efforts are aimed at providing alternative livelihoods for fishers impacted by fisheries management measures.
Legislative and Strategic Framework
- Rodrigues has enacted specific legislation to ensure the sustainable use of marine resources, including controls on octopus and sea cucumber harvesting and the regulation of sand mining activities through the Sand Mining Act of 1991.
- An Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) plan was implemented for Rodrigues as part of the broader strategy for the Republic of Mauritius, including tailored Action Area Plans for regions like Cotton Bay and Anse aux Anglais.
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) and Biodiversity Conservation
- Under the "Partnerships for Marine Protected Areas in Mauritius and Rodrigues" project, several marine reserves and a multiple-use marine park covering 59 square kilometers have been established to protect marine biodiversity. Measures such as a seasonal closure for octopus fishing align with the spawning season, enhancing population recovery and fishery sustainability.
Community Involvement and Environmental Projects
- Initiatives to foster alternative livelihoods prioritize environmental protection to support the economic well-being of local fishers, including incentives for fishers to shift away from environmentally harmful practices. Efforts include coral planting programmes to restore reefs damaged by bleaching and systematic planting of mangroves to reduce soil sedimentation within the lagoon, supporting the local ecosystems.
Challenges and Ongoing Initiatives
- Rodrigues continues to face challenges such as illegal fishing and sand mining. A technical committee monitors and regulates sand extraction activities to combat these issues effectively.
- Ongoing projects to enhance marine co-management and promote off-lagoon fishing aim to strengthen the resilience of the artisanal fishery sector.
Policy orientation and related strategies for marine and coastal resources in Rodrigues |
Table summarises the policy orientations and associated strategies designed to achieve Rodrigues' comprehensive objectives for managing its marine and coastal resources (Environment Masterplan, 2022).
# | Policy Recommendation | Strategy |
1 | To restructure the Fisheries Research and Training Unit into the Marine Academy and Research Centre. |
|
2 | To develop a strategic plan for the fisheries sector in Rodrigues. |
|
3 | Strengthen the fisheries sector with adequate staff and capacity building. |
|
4 | To sustainably exploit the unexploited off-lagoon resources. |
|


