Role of Dams and Reservoirs
The construction of dams and reservoirs across Mauritius is vital, providing a stable water supply and supporting agriculture, particularly in cultivating sugarcane and other crops. Additionally, the island's lakes and ponds play multiple roles, from supporting biodiversity to recreational activities.
Hydrology and Water Resource Management
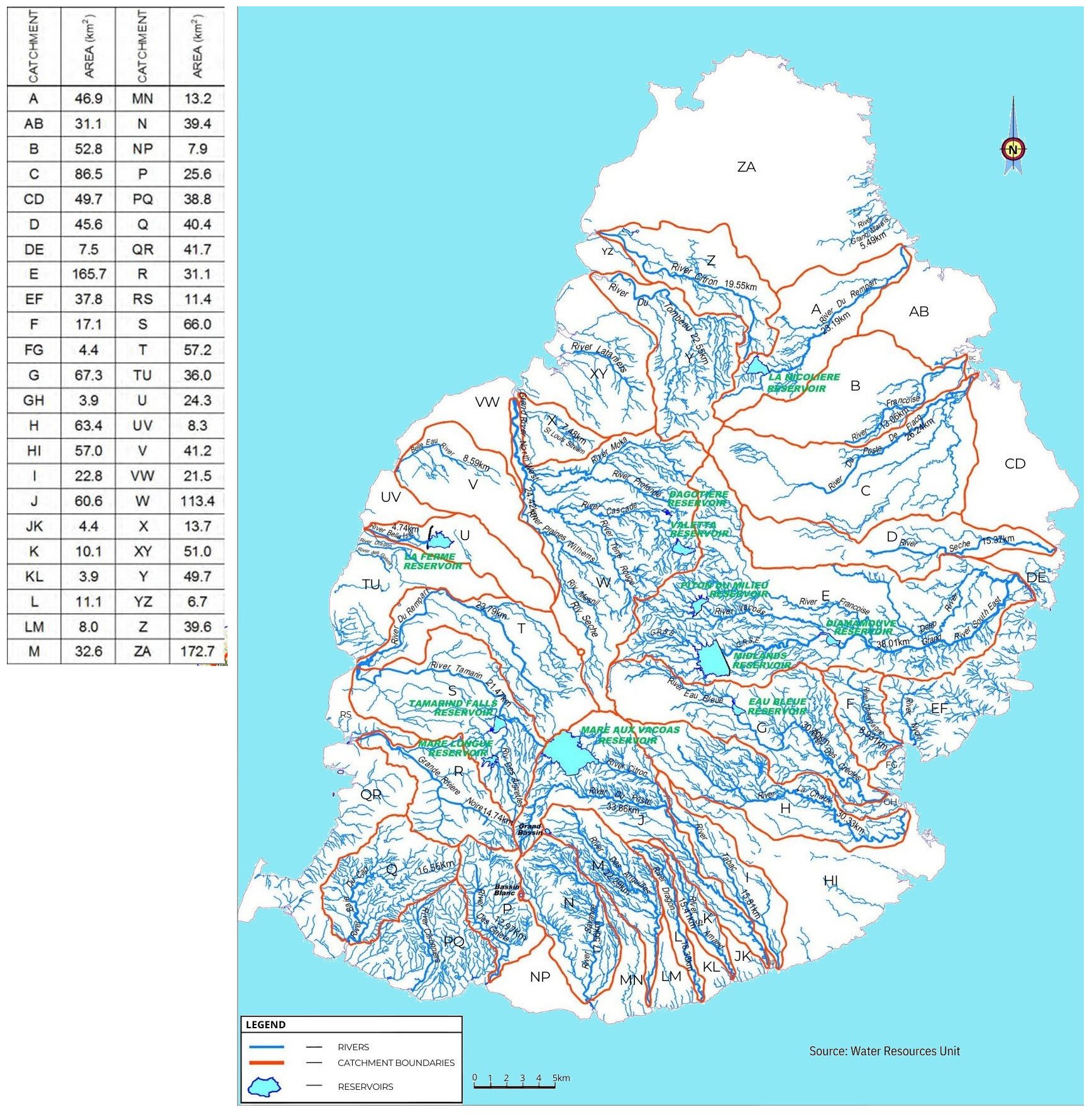
The hydrology of Mauritius is intricately defined by its diverse drainage patterns and water resource management. The island features major and minor drainage areas, with major areas having permanently flowing rivers. The northern part, known as the Northern Plain, exhibits minimal surface runoff due to its topography of young volcanic lavas, yet it's rich in groundwater which feeds many springs and wells.
Major Water Systems
Significant water systems include the Rivière du Rempart which feeds into the La Nicolière Reservoir, crucial for the northern irrigation networks, and the Grand River South East, the largest basin in Mauritius, which is highly influenced by groundwater and high rainfall. This river supports various uses including domestic supply, irrigation, and hydro-power through the Midlands Dam and other infrastructures.
Water Management in Central Uplands
In the central uplands, rivers like des Rivière des Créoles and Rivière Tamarin handle runoff from high rainfall areas, contributing to hydro-power and irrigation systems. Meanwhile, minor catchments like Plaine des Roches and Rivière Seche (East) have negligible surface runoff but are important for groundwater discharge.
Focus on Southern and Western Mauritius
The southern and western parts of the island focus on managing surface and groundwater flows for domestic, irrigation, and industrial purposes, with several reservoirs like Mare aux Vacoas and Tamarind Falls playing a critical role in water storage and management.