Aquatic Habitats are characterized by the presence of water and may be classified into two main types: Freshwater habitats and biodiversity:
Marine habitats and biodiversity:
| 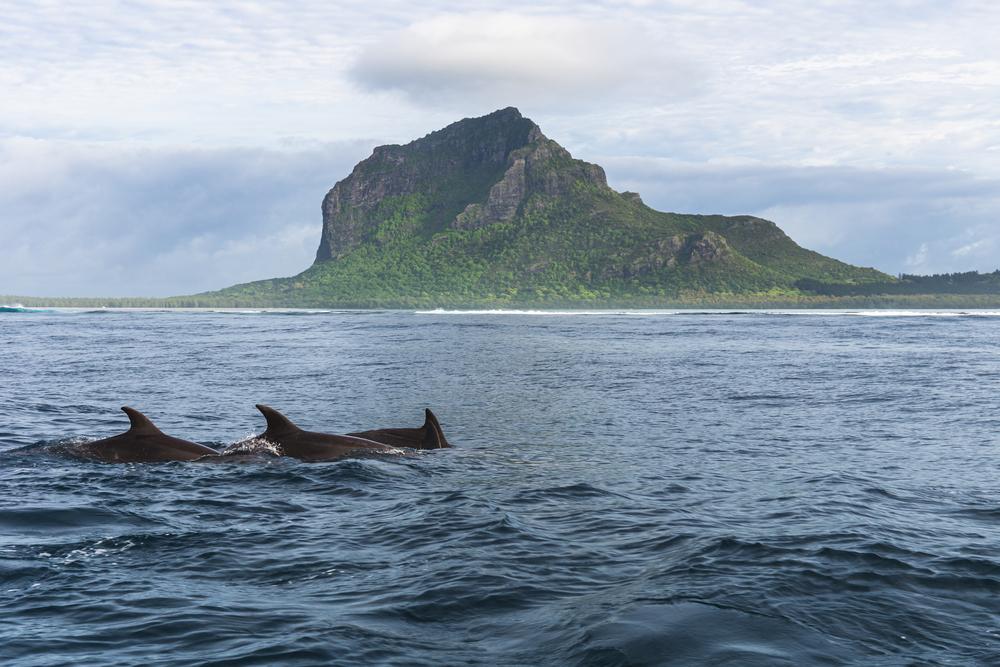 |
Aquatic Habitats are crucial since they underpin many environmental functions:
| A few facts and figures Mauritius, with a 322 km coastline and vast Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), boasts diverse ecosystems including sandy beaches, rocky shores, wetlands, and mangroves. The island's coral reefs, spanning about 150 km, include fringing reefs, patch reefs, atolls, reef flats, and barrier reefs. Biodiversity is rich, with over 160 marine algae genera and 36 seaweed species. Rodrigues has 493 fish species, 175 gastropod species, 104 algae species, 109 bivalve species, 138 coral species, 74 echinoderm species, and 41 bryozoan species. The islands also has two mangrove species, covering 181 hectares, and over 340 identified fish species. Source: (2016). Third National Communication: Report to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Republic of Mauritius | |
ThreatsAquatic habitats are often vulnerable to pollution, habitat destruction, and other human activities. Protecting these habitats is fundamental for sustaining these benefits and ensuring the well-being of both ecosystems and human communities that depend on them. More…
| ||
Conservation EffortsMauritius is dedicated to preserving its unique aquatic biodiversity through targeted conservation initiatives, including marine protected areas, reef restoration projects, and regulations to sustainably manage its endemic marine species. More… | ||


