Wetlands are vital ecosystems that are driven by the interactions between hydrology, biology, and soils. Wetlands play a vital ecological role in landscapes and are also among the Earth's most imperiled ecosystems. Many wetlands of Mauritius have been backfilled for touristic and housing development. The ecological condition of the remaining wetlands is being seriously challenged by numerous threats, natural and anthropogenic.
Biodiversity-Related ODE Sites:
- Rodrigues Biodiversity: Terrestrial (Flora; Fauna); Coastal & Marine;
- Mauritius Biodiversity: Terrestrial (Flora; Fauna); Coastal & Marine; Wetlands (this page);
- National Parks and Conservation Service: Flora; Fauna; Islet Biodiversity; Ramsar Sites - Wetlands; Protected Endemic Sanctuaries;
Wetlands can often be described as transitional zones that frequently occur between permanently flooded deep-water habitats and well-drained uplands, although they also include a diverse range of hydrological conditions and can exist independently of this gradient. Mauritius is blessed with both inland and coastal wetlands. Inland wetlands, which include freshwater lakes and marshes, play a critical role in regulating water flow, providing habitat for aquatic life, and supporting a wide range of waterfowl. These wetlands are integral to the island's hydrology and maintain water quality. The coastal wetlands of Mauritius, consisting of mangroves, seagrass beds, and estuaries, serve as crucial nurseries and breeding grounds for marine life. Mangroves, in particular, offer protection against coastal erosion and support the rich marine biodiversity of the region. Maintaining and conserving these wetland habitats are essential for the resilience of Mauritius's coastal ecosystems. |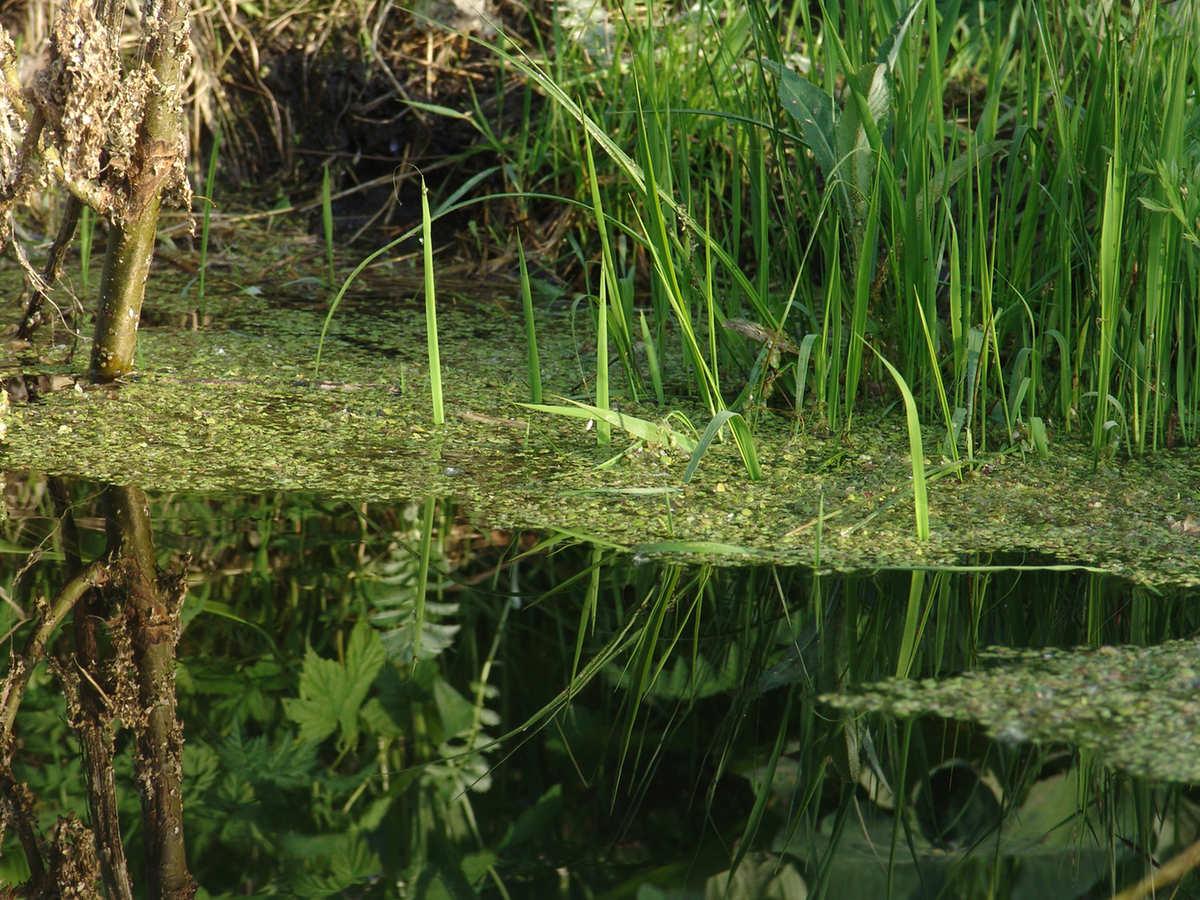  | |
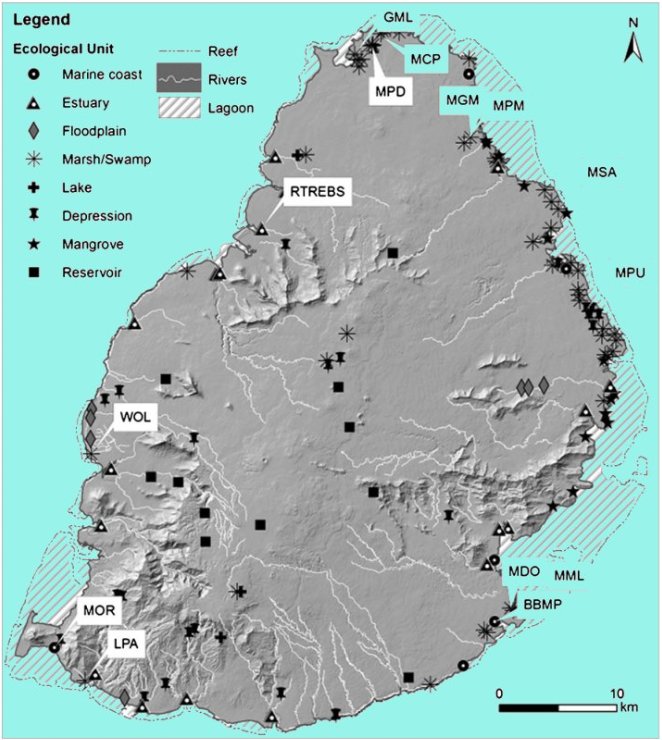
Wetlands TypesWetlands were identified and categorised into 8 ecological units Mamoun et al. (2013). Three of these wetlands are classified as Ramsar wetland. These are Blue Bay Marine Park (BBMP), Rivulet Terre Rouge Estuary Bird Sanctuary (RTREBS) and Pointe d'Esny Wetland. Laurance et al. assessed coastal wetlands for their biophysical attributes, land-use activities, and patterns of disturbance, to help identify factors that threaten wetland biodiversity. The latter reported that many wetlands faced edge-related disturbances, with over half being fragmented. Plant diversity was highest in large, unfragmented wetlands, but lower in those with degraded margins. Urban wetlands were smaller and more fragmented than those near grazing and agriculture. Flooding risk was higher near fragmented urban wetlands. Mauritius' ongoing wetland loss threatens local biodiversity and disrupts their ecosystem role in surface water regulation and marine habitat protection. Wetlands in Mauritius exhibit diverse characteristics and serve various ecological functions. Mauritius wetlands may be subdivided into the following categories (Mamoun et al., 2013; Laurance et al., 2012): Coastal Wetlands: There are over 200 coastal wetlands in Mauritius and Rodrigues (Technical Report on Freshwater Wetlands, 2010; Environmentally Sensitive Areas (ESAs), 2009).
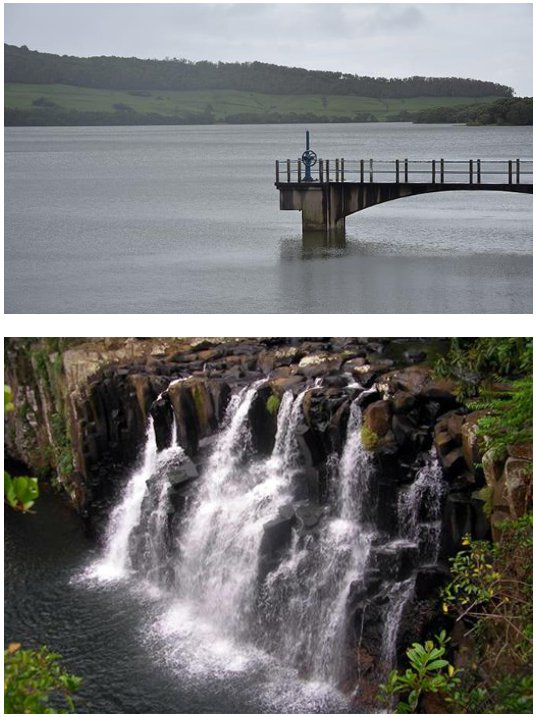
Inland Wetlands: These wetlands collectively contribute to the biodiversity, water resource management, and environmental health of Mauritius. They provide habitat for various species, support water purification, and play a crucial role in flood control, among other ecosystem services. Conservation and protection efforts are essential to ensure the continued well-being of these valuable ecosystems. Floodplains: These are low-lying areas adjacent to rivers and streams that periodically flood. They play a crucial role in absorbing and controlling floodwaters. The floodplain along the banks of the Rivière du Rempart is susceptible to seasonal flooding and helps regulate water flow during heavy rains. Lakes: Lakes are large bodies of standing freshwater. They can vary in size from small ponds to large, deep lakes. Grand Bassin, also known as Ganga Talao, is a natural crater lake in the highlands, considered a sacred site for the Hindu community. Marshes and Swamps: These are areas of standing water with emergent vegetation, but they differ in terms of the types of vegetation and water flow. Marshes typically have herbaceous plants, while swamps have woody vegetation. Bras d'Eau National Park contains marshes and wetlands, providing habitat for various bird species and other wildlife. Depressions: These are low-lying areas where water collects, often forming temporary or seasonal wetlands. Some low-lying areas within the Plaine Wilhems district fill with water during the rainy season, forming temporary depressions that are vital for waterflow. Ponds: Ponds are smaller, shallow bodies of water, typically smaller than lakes and often man-made. Pamplemousses Botanical Garden features ornamental ponds and water features within a lush botanical setting. Reservoirs: Reservoirs are human-made lakes, often created by damming rivers, for purposes such as water supply, hydroelectric power generation, and recreation. Mare aux Vacoas is a significant reservoir in the central part of the island, providing water for irrigation and domestic use. Rivers: While rivers are primarily flowing water bodies, they can have associated wetland areas along their banks and floodplains. The Rivière Noire, flowing through the Black River Gorges National Park, is a prime example of riverine wetlands with diverse aquatic life. Palustrine: Palustrine wetlands encompass various types of wetlands that do not fit into the above categories. They may include bogs, fens, and other wetland types. Mare aux Joncs is a palustrine wetland found in the Black River Gorges National Park, featuring distinct vegetation and aquatic species. |
|   |
Importance of Wetlands
Wetlands:
|
The Ramsar Wetlands
In September 2001, Mauritius adopted the Convention on Wetlands to protect and conserve the local marshes and to use them wisely is a sustainable way. Also called the Ramsar Convention (after the city in Iran in which it was first adopted), three sites of international importance were nominated in Mauritius. Wetlands consist of “areas of marsh, fen, peatland or water, whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six metres” (Ramsar Convention, Article 1.1). It “may incorporate riparian and coastal zones adjacent to the wetlands, and islands or bodies of marine water deeper than six metres at low tide lying within the wetlands” (Ramsar Convention, Article 2.1). The Ramsar Convention is an intergovernmental treaty that provides the framework for national action and international cooperation for the conservation and wise use of wetlands and their resources. As a prerequisite to Ramsar Convention, the Government has set up a National Ramsar Committee comprising members from all relevant institutions involved with wetlands to assist the Ministry in implementing the provisions contained in the Ramsar Convention as well as advise on Wetland development issues. As at date, three Ramsar Sites of international importance have been proclaimed in Mauritius. They are: 1. Rivulet Terre Rouge Estuary Bird Sanctuary on 30 September 2001 2. Blue Bay Marine Park on 31 January 2008 3. Pointe d’Esny on 16 September 2011 The Ramsar wetlands are the Rivulet Terre Rouge Estuary Bird Sanctuary (26.4 ha), the Blue Bay Marine Park (353 ha) and the Pointe D’Esny Wetland (22 ha). |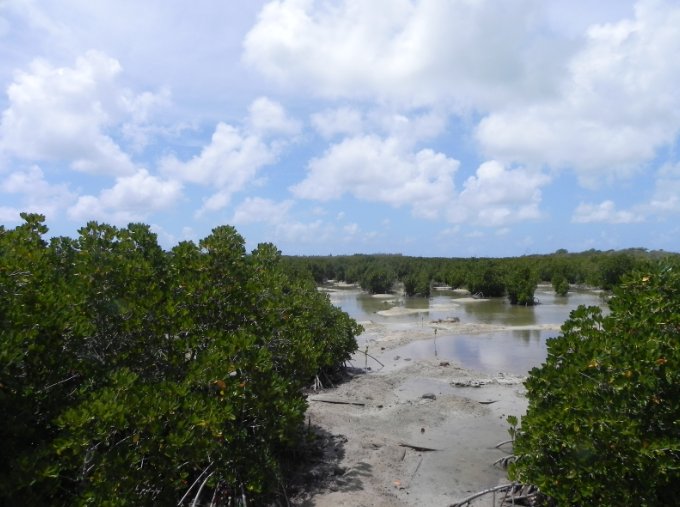  |
Wetlands Biodiversity
More..(NPCS, Mauritius) FLORA The two main plant species that grow in our coastal wetlands are the mangroves:
Mangroves provide a unique and specialized habitat, which is in part due to the complex root systems and the intertidal nature of mangrove ecosystems. They play a significant role in supporting a diverse range of species including: FAUNA
|  |
Conservation and Sustainable Use of Wetlands
Mauritius has implemented several acts and regulations directly or indirectly related to wetland protection and environmental conservation:
These acts and regulations collectively contribute to the protection and conservation of wetlands in Mauritius by addressing various aspects of land and resource management, environmental impact assessment, and conservation planning. It's important to consider their interplay in ensuring the sustainable management and protection of wetland ecosystems. In addition to these acts, Mauritius also implements international agreements and conventions related to wetland protection, such as the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands, which designates specific wetlands of international importance within the country and commits Mauritius to their conservation and sustainable use. |


